Your Trusted Supplier for Compostable Waste Solutions!
Compostable vs Biodegradable: What's the Real Difference
In recent years, the push for sustainability has led to a surge in the popularity of eco-friendly products. As consumers become more conscious of their environmental impact, many are turning to alternatives like compostable bags and biodegradable packaging to reduce waste. But while the terms “compostable” and “biodegradable” are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. Understanding the real difference between compostable and biodegradable materials is essential for making informed decisions—whether you’re a business owner seeking eco-friendly waste solutions or a consumer interested in sustainable living.
In a world full of eco-labels, it’s easy to get confused between terms like “compostable” and “biodegradable.” While both sound environmentally friendly, they don’t mean the same thing—and understanding the difference is key to making the right choice for your business or home. At ECO BLOOM, we believe in educating our customers so they can choose products that truly make a difference. So let’s break it down.
What Does Biodegradable Mean?
Biodegradable refers to any material that can be broken down naturally by microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, and algae. These organisms help decompose the product into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass over time. At first glance, this sounds perfect—but the term “biodegradable” can be misleading.
Many biodegradable products take years, even decades, to fully decompose, especially in landfills where oxygen and sunlight are limited. Just because something is labeled biodegradable doesn’t mean it breaks down quickly or safely. In fact, some so-called biodegradable plastics only degrade into smaller microplastics, contributing to pollution rather than solving it.
This is why understanding how and where a biodegradable item will break down is crucial. For example, a biodegradable straw might still exist in a landfill for decades without the right environmental conditions. Therefore, while biodegradable products are a step in the right direction, they’re not always the most efficient or eco-friendly waste solution.
What Does Compostable Mean?
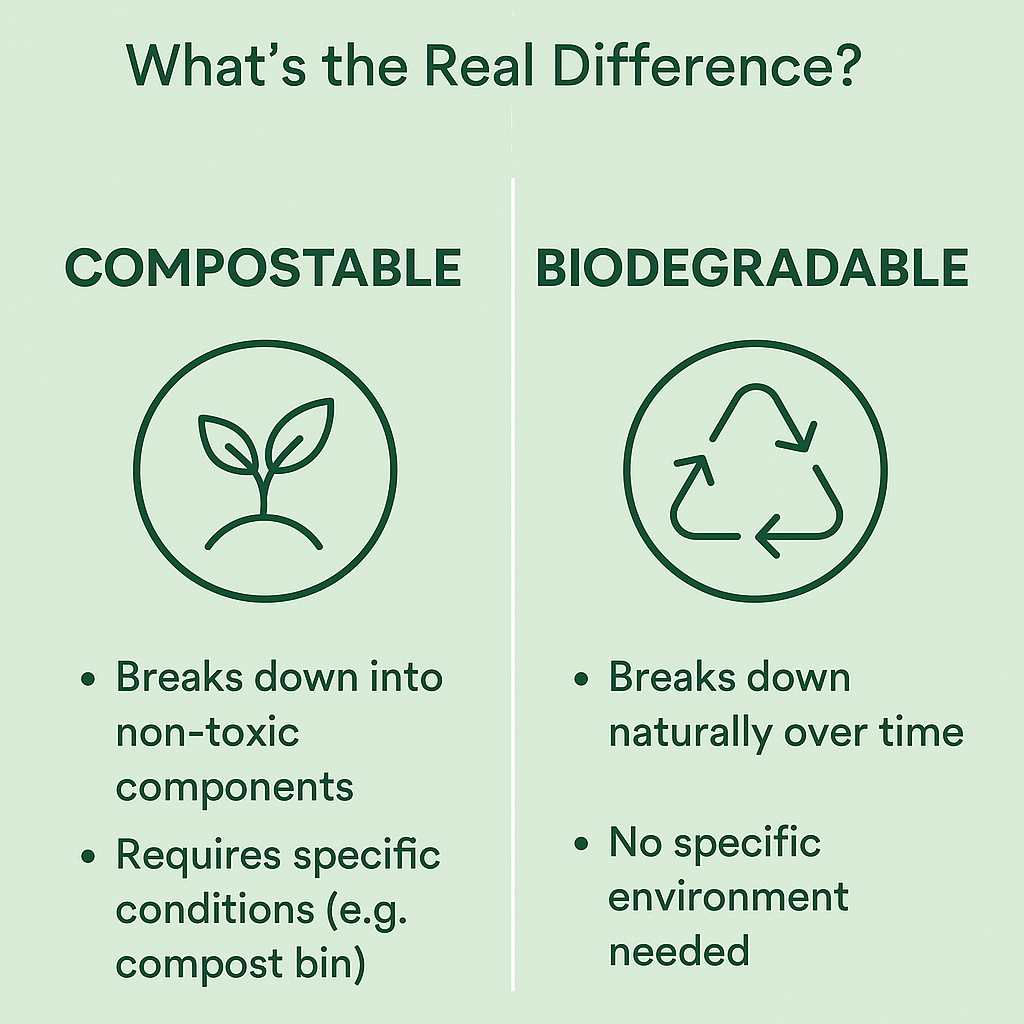
Compostable materials go one step further than biodegradable ones. A compostable product not only breaks down naturally, but it also turns into nutrient-rich compost when disposed of in the right conditions. These conditions usually involve a controlled composting environment with specific levels of heat, moisture, and oxygen.
Unlike biodegradable items, compostable materials decompose within a relatively short period—typically around 90 days—without leaving behind any harmful residues. They break down into water, carbon dioxide, and organic matter that benefits the soil. This makes compostable products an ideal solution for food waste, yard clippings, and other organic materials.
What sets compostable items apart is their ability to contribute positively to the environment by enhancing soil quality. Composting reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and promotes healthier plant growth. For this reason, many municipalities and businesses are shifting toward compostable bags and compostable packaging as part of their sustainability initiatives.
Key Differences Between Compostable and Biodegradable
To make a truly eco-friendly choice, it’s important to distinguish between the two terms beyond surface-level similarities. Below are the main differences that help you make informed decisions when choosing between compostable and biodegradable products.
Decomposition Time
Compostable items usually break down in less than 90 days, while biodegradable items may take several years to fully decompose.
End Result
Compostable materials turn into safe, nutrient-rich compost that enhances soil. In contrast, biodegradable materials may leave behind toxins or microplastics if not properly managed.
Conditions Required
Compostable products need specific conditions—such as those found in industrial composting facilities—to decompose effectively. Biodegradable products may break down in natural environments, but the process is often slower and less reliable.
Certifications
Compostable products often come with third-party certifications such as BPI, ASTM D6400, or EN 13432. These certifications ensure the product meets safety and performance standards for composting.


Proudly supplying eco-friendly, compostable bin liner/garbage bags to businesses across Canada. Committed to sustainability, customer satisfaction, and a greener tomorrow.
☎️ Phone: +1 (647) 772-5449
✉️ Email: sales@ecobloom.ca
Compostable Bin Liners
© 2025 Eco Bloom. All rights reserved. | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions